Navigating the Intersection of Environmental Health and Safety
As we advance into an era where environmental awareness is becoming paramount, the concepts of Environmental Health and Safety (EHS), occupational protection, and environmental sustainability are gaining significant traction. These fields are no longer standalone disciplines; rather, they intertwine to form a collective framework aimed at ensuring human health and ecological integrity. Understanding this intersection is essential for organizations, communities, and individuals alike.
Defining Environmental Health and Safety (EHS)
Environmental Health and Safety is a comprehensive discipline that seeks to address the nexus of environmental factors and their impacts on human health. It takes into account how the condition of our surroundings—ranging from air quality to chemical exposure—affects our well-being. At its core, EHS promotes safe working environments, sustainable practices, and proactive measures to mitigate risks that threaten public health and the environment.
Key components of EHS include:
- Workplace Safety: This encompasses the identification and management of health hazards in occupational settings, ensuring that workers are protected from physical, chemical, and biological risks.
- Environmental Stewardship: This facet focuses on responsible management of resources and ecosystems, aiming to reduce pollution and conserve biodiversity.
- Community Well-Being: EHS practices extend beyond workplaces, influencing broader community health through initiatives aimed at clean air, water, and the reduction of hazardous waste.

The Crucial Role of OSHA
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is a fundamental player in the realm of workplace safety. Founded to ensure safe and healthy working conditions, OSHA develops regulations, provides training, and enforces compliance across various sectors.
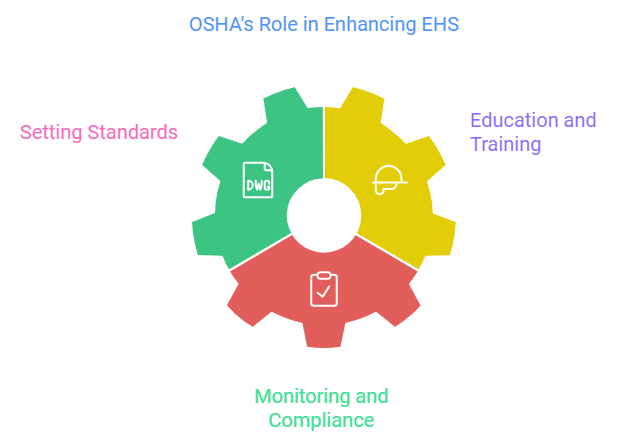
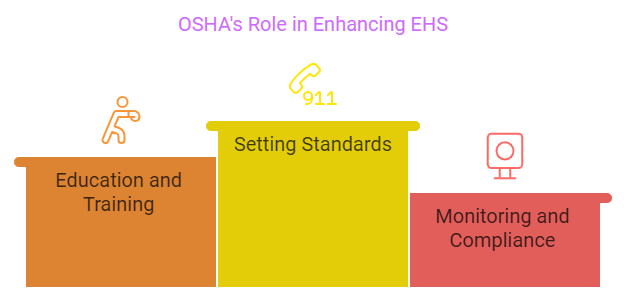
How OSHA Enhances EHS:
- Setting Standards: OSHA establishes legally binding standards that dictate how workplaces can manage hazards. These guidelines help organizations create safer environments, reducing the likelihood of accidents and illnesses.
- Education and Training: ThroughHow OSHA Enhances EHS: comprehensive workshops and resources, OSHA equips both employers and employees with essential knowledge regarding safety protocols and hazard recognition.
- Monitoring and Compliance: OSHA's commitment to inspecting workplaces and enforcing standards serves as a deterrent against unsafe practices, fostering a culture of accountability in workplaces.
Learn Health and safety
Emphasizing Environmental Protection
Environmental protection complements EHS by focusing on the preservation of natural resources and ecosystems. This includes initiatives aimed at combating climate change, reducing waste, and using natural resources sustainably.
Core Aspects of Environmental Protection:
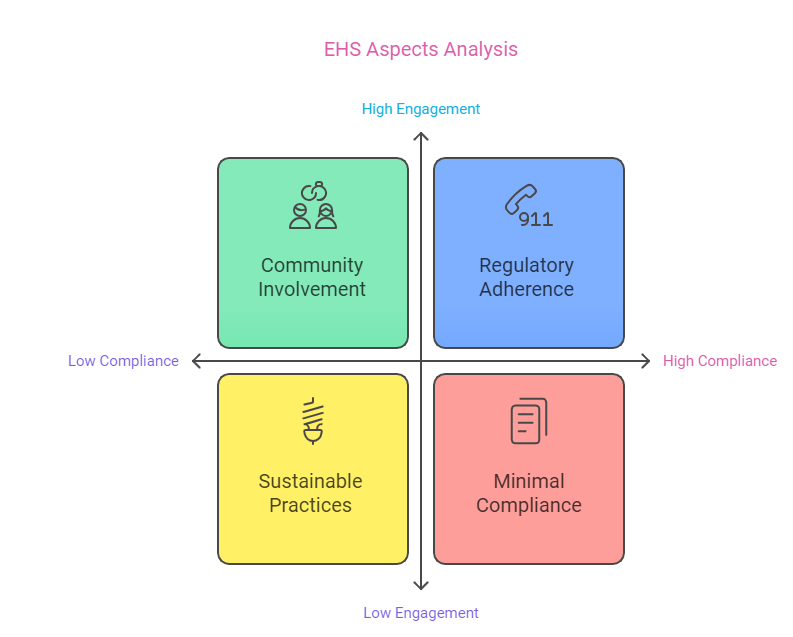
- Regulatory Compliance: Environmental Protection Agencies (like the EPA in the United States) set regulations that organizations must follow to minimize their environmental impact. These regulations often overlap with OSHA guidelines, promoting holistic safety at work.
- Sustainable Practices: Companies are increasingly adopting sustainable practices such as reducing carbon footprints, utilizing renewable energy, and innovating in waste management. These efforts contribute not only to environmental preservation but also enhance employee morale and public perception.
- Community Engagement: Effective environmental protection often requires community involvement. Engaging local populations in decision-making processes ensures that environmental health efforts reflect the needs and values of the community.
Creating Synergy Between EHS, OSHA, and Environmental Protection
The interplay between EHS, OSHA, and environmental protection is essential for promoting a safe and healthy society. Here is how they work synergistically:
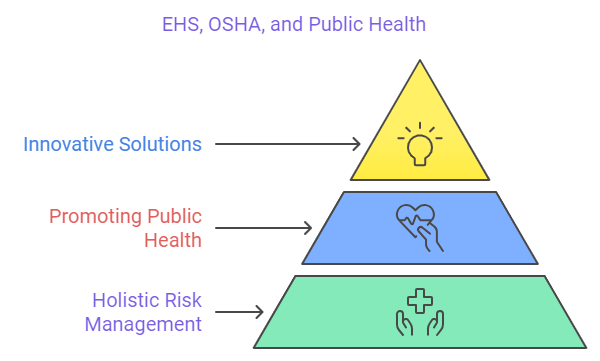
- Holistic Risk Management: Organizations that integrate EHS practices with OSHA standards can effectively identify and mitigate risks, leading to safer workplaces and healthier communities.
- Promoting Public Health: By addressing environmental hazards, organizations reduce the likelihood of health issues not only for workers but also for the surrounding community, generating a cascading effect that benefits public health.
- Innovative Solutions: Collaboration between employers, regulatory agencies, and environmental organizations encourages the development of innovative solutions to complex health and environmental challenges.
Conclusion
The comprehensive framework of Environmental Health and Safety highlights the importance of understanding our interconnectedness with the environment. By embracing EHS principles, complying with OSHA regulations, and committing to robust environmental protection efforts, we can build a healthier, safer world.
As we move forward, organizations and individuals alike must prioritize these principles, fostering a culture of safety, sustainability, and responsibility. In doing so, we not only protect the well-being of ourselves and our communities but also contribute to the health and resilience of our planet for future generations. By advocating for responsible practices, we can navigate the challenges ahead and create a thriving environment that benefits everyone.